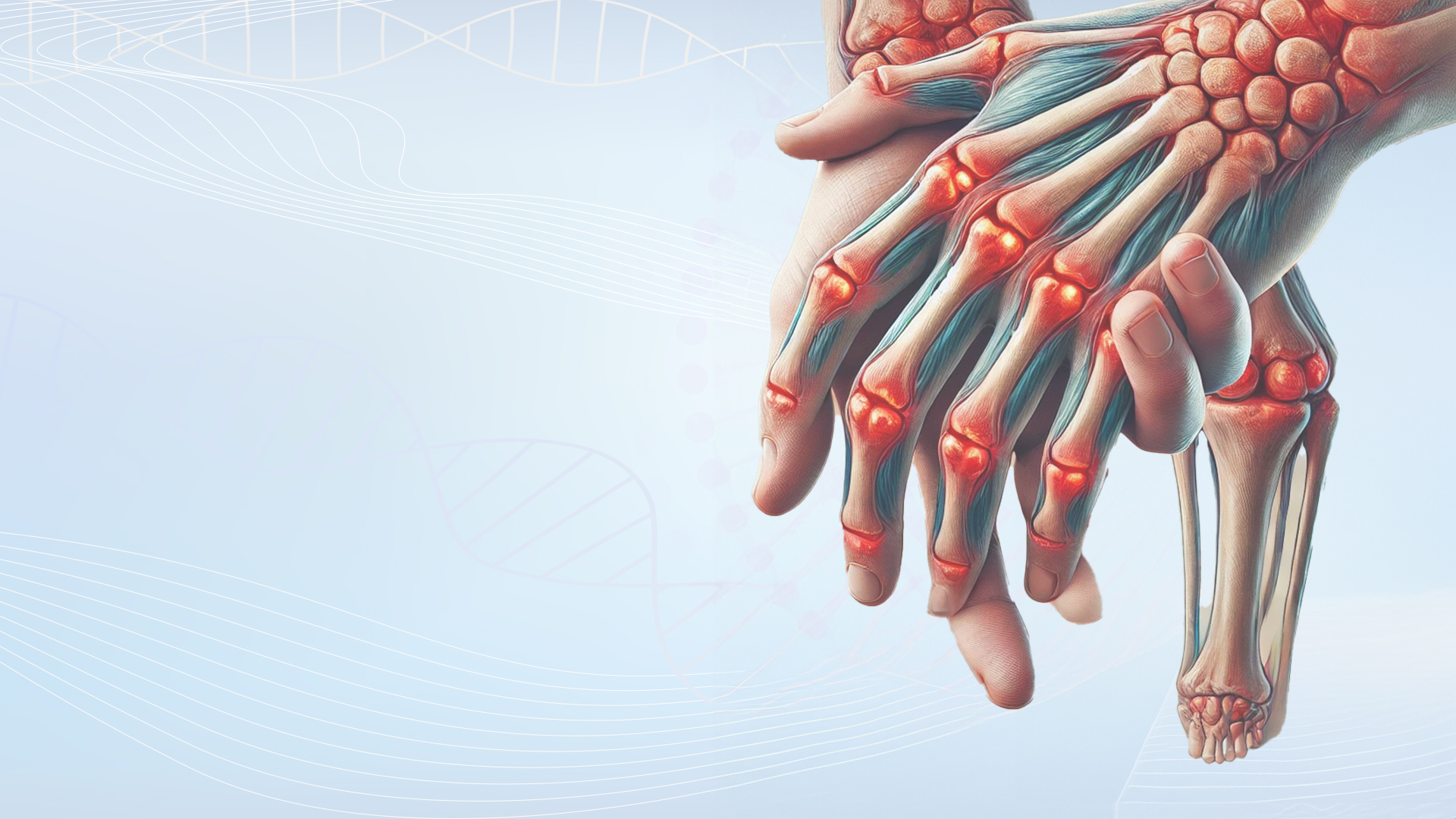
Rheumatoid Arthritis
The information given below does not contain health advice. If you are considering this procedure, you should consult a doctor. Click here to see the health facilities and doctors providing this service on the HealthTürkiye portal.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic, autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy body tissues. While the immune system normally protects the body against infections and foreign substances, in RA, certain body tissues, especially joints, are targeted. This attack causes inflammation, pain, swelling and, over time, permanent damage to the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis often starts in the joints of the hands and feet and usually affects joints symmetrically, which means it affects joints on both sides of the body at the same time. RA not only affects the joints, but can also affect other organs such as the skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels.
The disease is chronic, meaning it is long-term and can last a lifetime. The cause of RA is not known for certain, but it is thought to occur as a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Although RA is not a curable disease, it is possible to control symptoms and slow the progression of the disease with modern treatment methods.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact causes of rheumatoid arthritis are not fully understood, but many factors are thought to play a role in the development of this disease. In RA as an autoimmune disease, the immune system reacts against the body's own tissues, which causes inflammation in the joints. Research shows that both genetic predisposition and environmental triggers can initiate this autoimmune process.
- Genetic Factors: People with a family history of RA have an increased risk of developing this disease. There are certain genetic markers known to be associated with RA. In particular, genetic variations such as HLA-DR4 are thought to increase the risk of developing RA. Genetic predisposition can affect how the immune system works and can predispose a person to autoimmune diseases.
- Environmental Factors: There is evidence that some environmental factors also play a role in triggering rheumatoid arthritis. These include smoking, obesity, infections and certain hormonal changes. Smoking in particular has been found to be an important risk factor in the development of RA. Smokers have a higher risk of developing RA than non-smokers and smoking can make the disease more severe. It is also thought that some infections can trigger the immune system and lead to RA.
- Hormonal Factors: RA is more common in women than in men, suggesting that hormonal factors may play a role in RA. Especially the effects of estrogen hormone on the immune system are being investigated. The fact that the disease is more common in women suggests that hormonal changes (e.g. pregnancy, postpartum period or menopause) may be influential in the development of RA.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease, it usually flares up at certain periods and may have occasional periods of remission. Symptoms vary from person to person, but the disease is characterized by joint pain, stiffness and swelling. The most common symptoms of RA are:
- Pain and swelling in the joints: The most basic symptom of rheumatoid arthritis is pain, swelling and tenderness in the joints. This swelling occurs as a result of inflammation of the synovial tissue around the joint. Synovial tissue is a membrane that surrounds the joints and produces fluid that facilitates joint movements. When this membrane becomes inflamed, it causes pain and restricted movement in the joint. The pain is usually more noticeable in the morning or after a long period of inactivity.
- Joint stiffness: One of the characteristic features of RA is joint stiffness in the morning. This stiffness may persist for several hours after waking up in the morning in RA patients and it may become difficult to move the joints. Morning stiffness is an indicator of joint inflammation and a hallmark symptom of RA.
- Fatigue and weakness: RA can affect not only the joints but also overall body health. Patients often feel tired, fatigued and weak. This fatigue occurs as a side effect of the inflammatory process. Chronic inflammation can deplete the body's energy resources and lead to a general feeling of weakness.
- Fever and weight loss: Since RA is a systemic disease, patients may occasionally experience generalized symptoms such as low-grade fever and involuntary weight loss. These symptoms are a general response of the body to inflammation.
- Joint deformation: As the disease progresses, permanent joint damage and deformation can occur. This is particularly noticeable in the hands and feet. Fingers may bend, joints may swell and loss of function may occur. In advanced cases, patients may have difficulty performing activities of daily living.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
Rheumatoid arthritis can sometimes be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms may initially be similar to other joint diseases. The diagnostic process is based on the patient's medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests and imaging methods. Early diagnosis is very important to prevent the disease from progressing.
- Medical History and Physical Examination: When doctors suspect RA, they take the patient's medical history and evaluate the symptoms. Findings such as which joints are affected, duration of pain and swelling, joint stiffness in the morning are evaluated. In the physical examination, the doctor examines swelling, tenderness and deformations in the joints.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests commonly used to diagnose RA include rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody tests. These antibodies are found in most patients with RA and are helpful in diagnosing the disease. However, not all RA patients may be positive for these antibodies. Inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are also used to measure the activity of RA.
- Imaging Methods: Methods such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound are used to assess damage and inflammation in the joints. Joint changes that cannot be detected by X-ray in the early stages can be visualized in more detail with MRI and ultrasound. These methods are important for monitoring the course of the disease and assessing response to treatment.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Methods
The aim of treating rheumatoid arthritis is to relieve symptoms, control inflammation and prevent joint damage. Treatment usually consists of medication, lifestyle changes, physical therapy and, in some cases, surgery. Starting treatment early is critical in slowing the progression of the disease.
- Medication Therapy: Medications used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis are used to prevent joint damage and relieve symptoms by reducing inflammation. Medications are selected according to the severity of the disease and the general health status of the patient:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs are used to reduce pain and inflammation. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are effective in relieving joint pain, but they do not stop the progression of the disease.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are used in short-term treatments for their strong anti-inflammatory effects. However, they should be used with caution in long-term use due to the risk of side effects (osteoporosis, weight gain, diabetes, etc.).
- Disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These drugs suppress the immune system to control inflammation and prevent joint damage. Methotrexate is one of the most widely used DMARDs and is considered one of the keystones of RA treatment.
- Biologic therapies: Biologic agents control inflammation by targeting specific proteins in the immune system. Biologic agents such as TNF inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors and B cell therapies have revolutionized the treatment of RA. These drugs can change the course of the disease and control symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy and rehabilitation play an important role in maintaining joint mobility and improving muscle strength in patients with RA. Physiotherapists help reduce joint stiffness and strengthen muscles by creating specific exercise programs for patients. Regular exercise can reduce pain in the joints and improve overall health.
- Lifestyle Changes: When managing rheumatoid arthritis, lifestyle changes can support the treatment process. A balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep and avoiding stress can be effective in managing the disease. Especially quitting smoking can slow down the progression of RA.
- Surgical Intervention: In advanced stages of RA, permanent joint damage may occur. In these cases, surgical interventions such as joint replacement or joint repair may be necessary. Surgery can improve patients' quality of life and restore joint function.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease that significantly affects quality of life. The disease can lead to permanent damage to joints over time, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, this damage can be prevented. Various methods such as medication, physical therapy and lifestyle changes can be used to manage the symptoms of RA and stop the progression of the disease. Due to the nature of the disease, it is important that patients with RA work closely with their doctor and have regular checkups. This way, patients can keep their symptoms under control and lead a more active life.
Why choose HealthTürkiye?
Türkiye has become a sought-after destination for medical tourism, thanks to its well-established healthcare system and highly trained medical professionals. HealthTürkiye, an official representative of the Türkiye healthcare system, has been authorized by the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Türkiye to assist international travelers seeking medical care in Türkiye. USHAŞ is a government-affiliated organization that makes it easier for international travelers to get the right direction and guidance for medical services. HealthTürkiye offers specialized services to guide patients from all over the world in accessing top-quality medical services in Türkiye.
HealthTürkiye provides a wide range of medical facilities and advanced technology to ensure that patients receive the best possible care. The organization collaborates with the foremost hospitals in the field to develop personalized treatment plans for each patient, considering their specific needs and preferences. The medical professionals at these hospitals are highly trained and experienced, ensuring that patients receive safe, effective, and high-quality care.
Building on the achievement of HealthTürkiye, Türkiye strives to position itself as the greatest global center for healthcare services. By prioritizing inclusive and readily available healthcare services, as well as embracing cutting-edge technology and specialized knowledge, Türkiye has emerged as an appealing destination for individuals seeking medical tourism opportunities.
If you would like to benefit from Türkiye's healthcare services, HealthTürkiye will meet you the best medical care.


